Натяжные потолки стали популярным элементом современного интерьера, благодаря их эстетической привлекательности и функциональности.
Организация автономной канализации в частном доме является ключевым элементом комфортного и экологичного проживания. Это
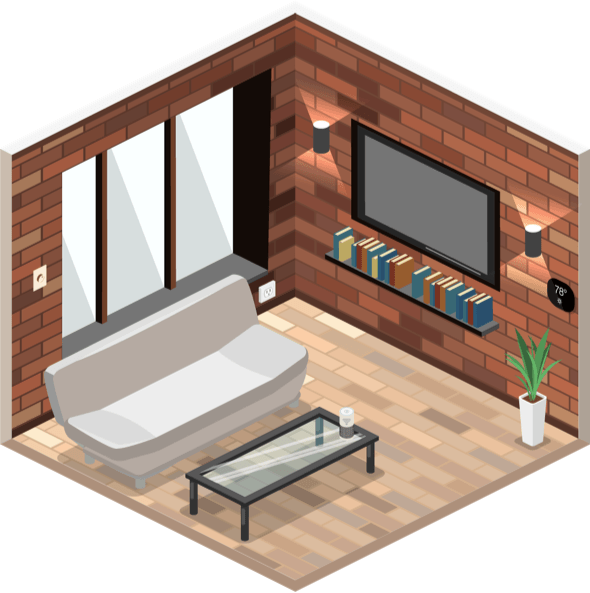
Дизайн интерьера включает в себя ряд ключевых аспектов, каждый из которых играет свою роль
Стиль лофт, возникший в середине XX века, сегодня популярен во всем мире. Он идеально
При выборе светильников важно учитывать не только их дизайн, но и технические характеристики, такие
Компания АО "ГРАД" предлагает полный спектр услуг по установке наплавляемой кровли, обеспечивая качество и
Основные положения работы компенсационного фонда определяются саморегулируемой организацией на основе своих уставных документов и
Интерьер в стиле неоклассика является прекрасным сочетанием изысканной элегантности и художественной гармонии. Отсылая к
XCMG (Xuzhou Construction Machinery Group) - один из крупнейших китайских производителей строительной и дорожной
Мастерская Уюта - это магазин сантехники в Алматы, предлагающий широкий ассортимент товаров для ванной
Нержавеющий металлопрокат – это востребованный материал, обладающий уникальными свойствами, которые делают его незаменимым во
Аренда специализированной техники – это процесс временного использования технического оборудования или машин для выполнения
Фурнитура и комплектующие для мебели играют важную роль в создании функциональных и эстетически привлекательных
Магнитные сепараторы - это специальные устройства, используемые для разделения магнитных материалов на основе их
Двери – это один из самых важных элементов в квартире, они обеспечивают безопасность, комфорт
Стеклянные столы стали популярным выбором для интерьера благодаря их элегантному внешнему виду и прочности.
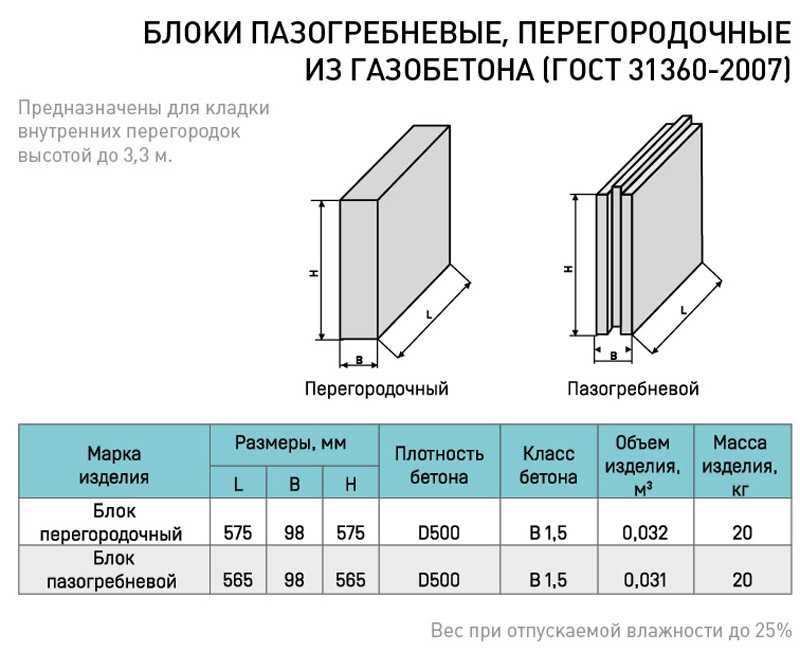
Какова звукоизоляция ПГП плит производимых в России основными производителями. Что такое звукоизоляция и каковы
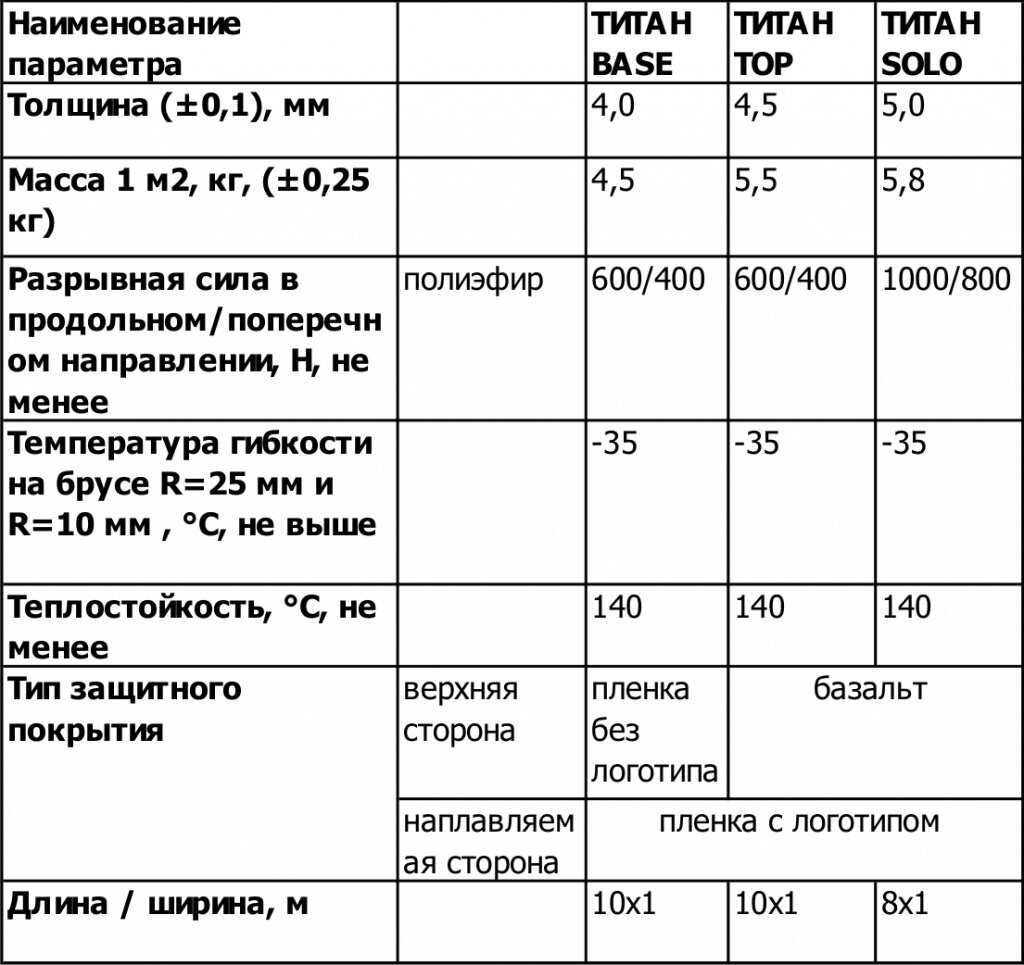
Информация про основные характеристики и особенности применения клея Титан.
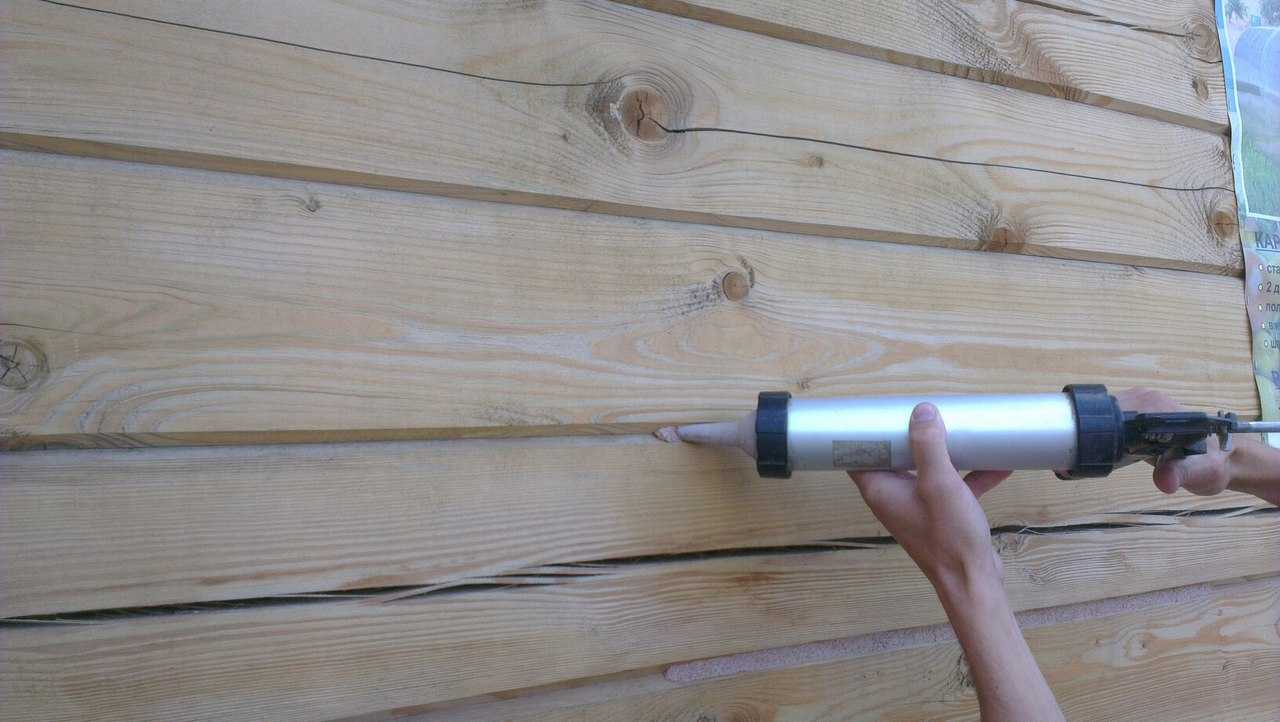
Пробковый герметик можно использовать для настила полов, заделывания любых щелей и стыков — после
Широкоформатные зеркальные панели на стену можно встретить только в современных интерьерах. О правилах и
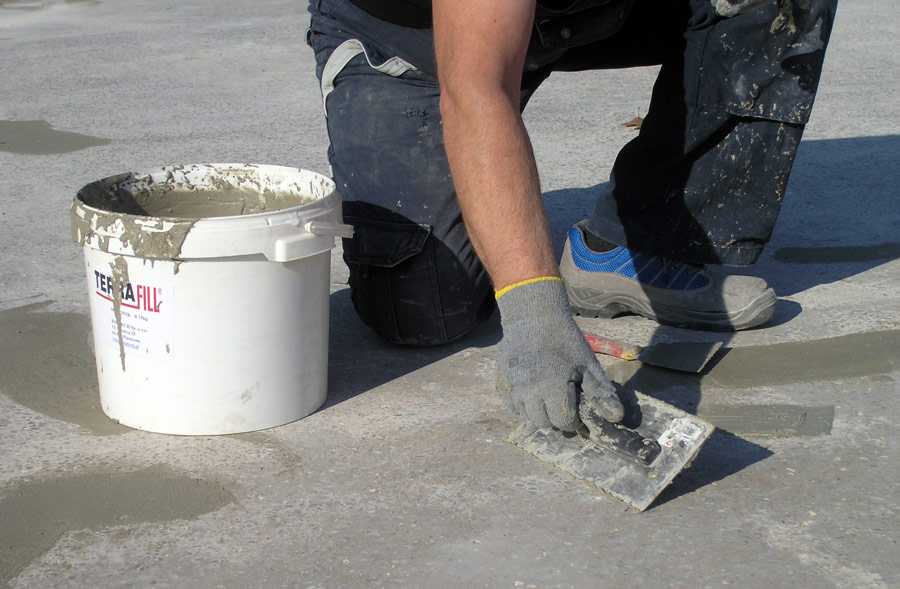
Учимся делать железнение бетона для поверхности пола, дорожек, стяжек и других вариантов. Приводим пропорции
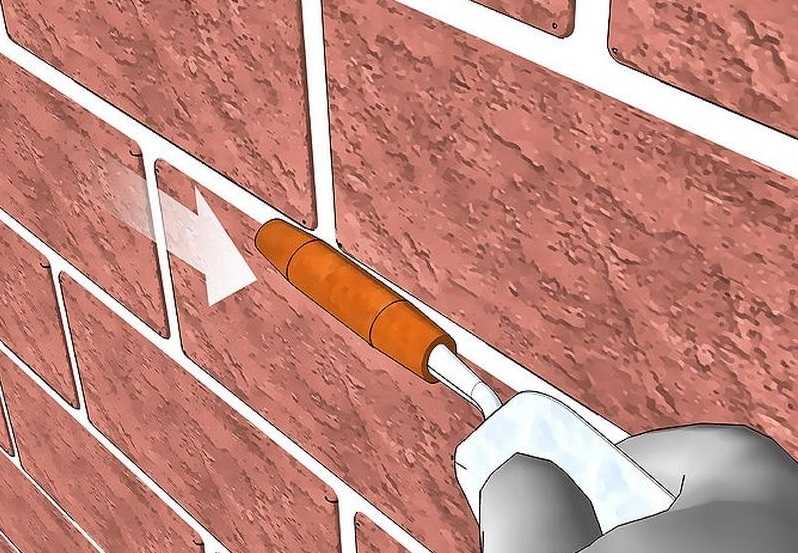
Узнайте, как выполняется затирка швов кирпичной кладки! Обзор способов и видов, инструкция по затирке
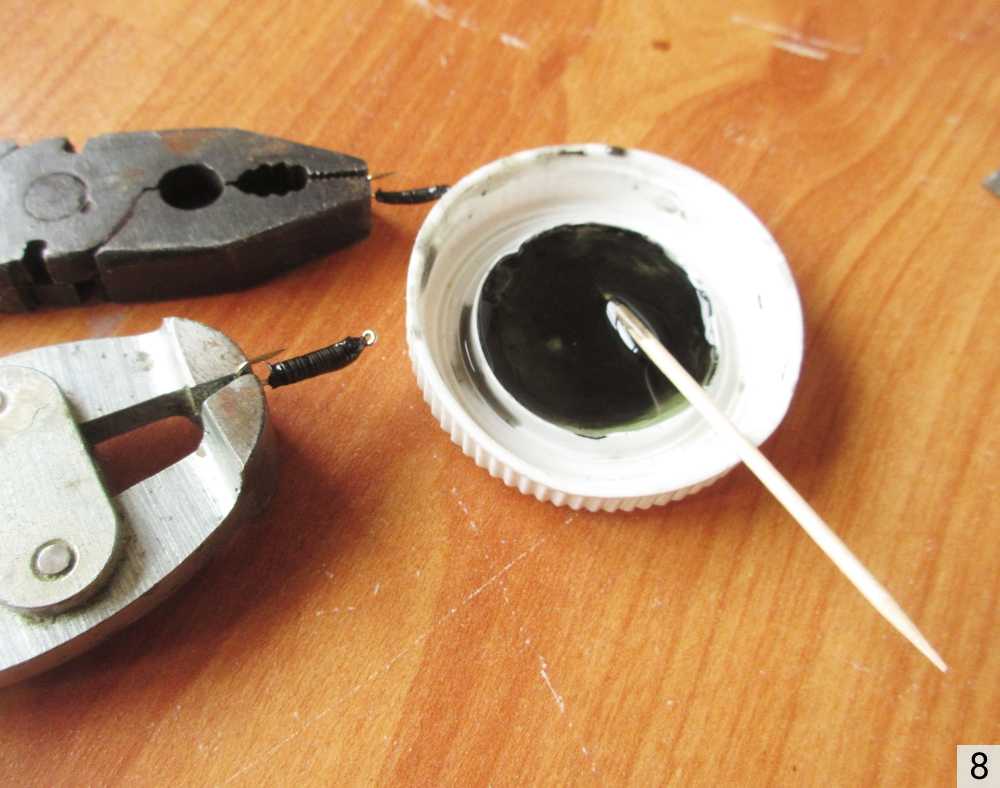
Заклепки своими руками Как сделать заклепки из проволоки своими руками Очень часто нужно что-то
Клепка – процесс выполнения неразъемного соединения листов металла с использованием заклепок. Такой вид соединений
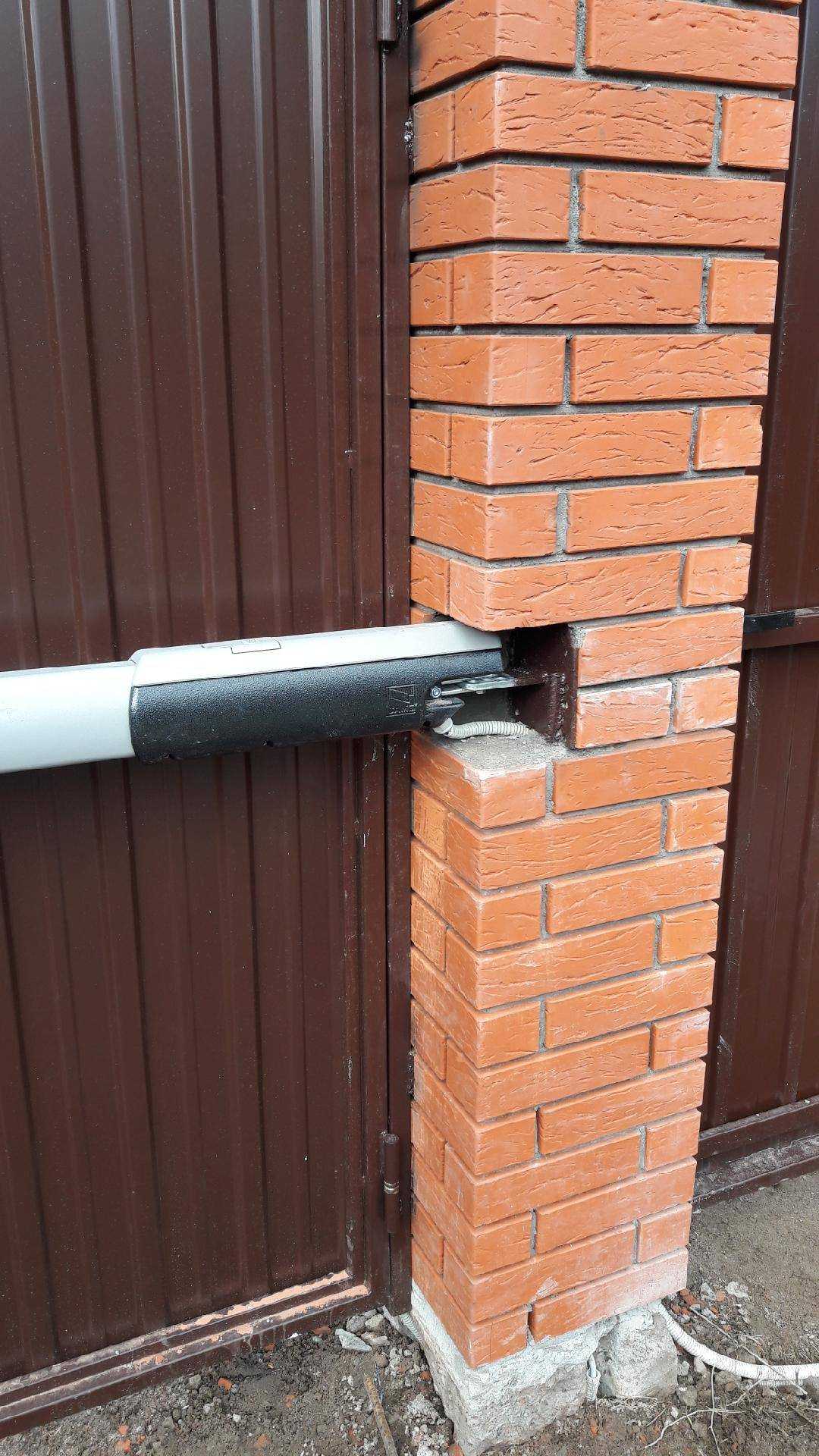
Как сделать кирпичные столбы для ворот и какие использовать закладные при их креплении.
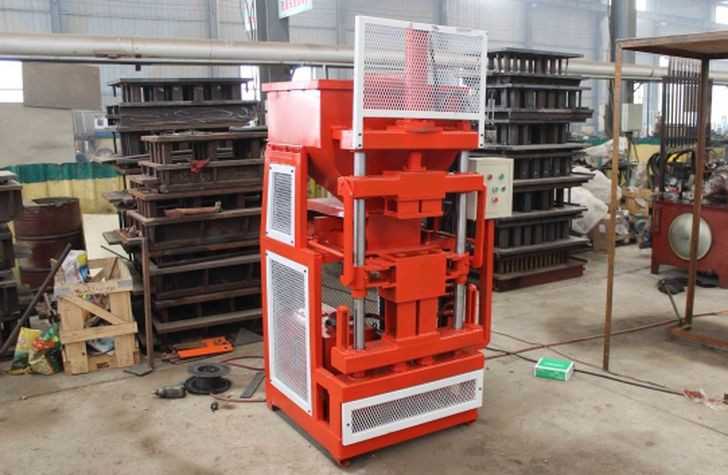
Можно организовать производство кирпича лего своими руками, тем самым ускорить и упростить стройку. Для
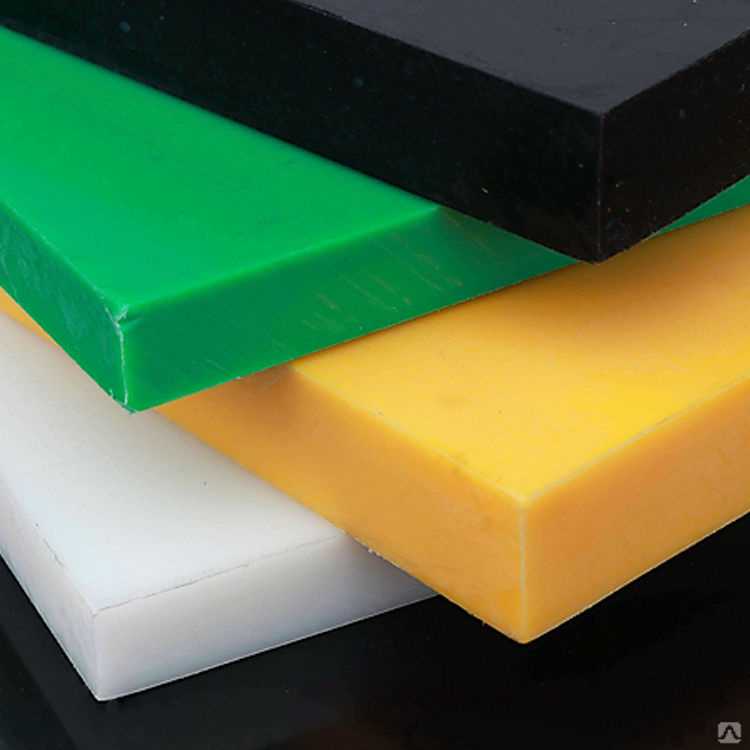
Получают вспененный полиэтилен листовой методом экструзии. Благодаря своим свойствам он нашёл применение в строительстве
Статья о тугоплавком металле вольфрам. Рассматривается процесс получения компактного вольфрама из руды, основные виды
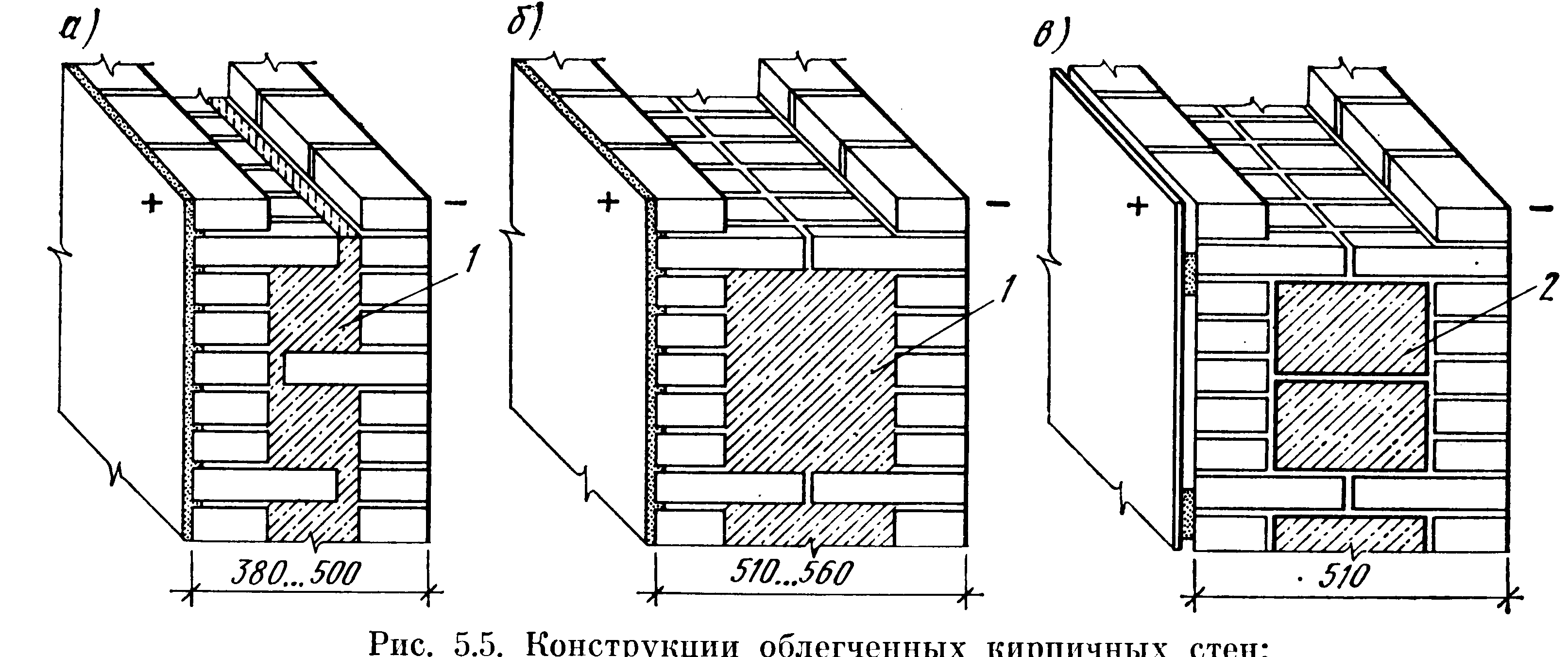
Колодцевая кладка стен из кирпича является несложным и хорошим методом утепления при возведении жилого дома. Этот
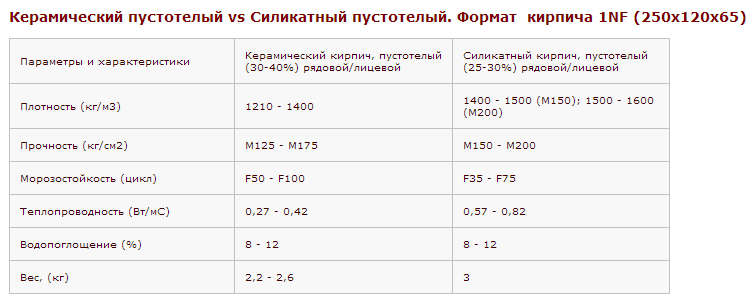
Зная вес поддона с кирпичом, можно рассчитать, сколько можно погрузить на транспорт для перевозки стройматериала изделий,